In a normal distribution,
68% (34%+34%) of the results fall within one standard deviation, and 95%
(68%+13.5%+13.5%) fall within two standard deviations. At the center (the 0
point in the image above) the median (the middle value in the set), the mode (the value that
occurs most often), and the mean (arithmetic average) are all the same.
Summary
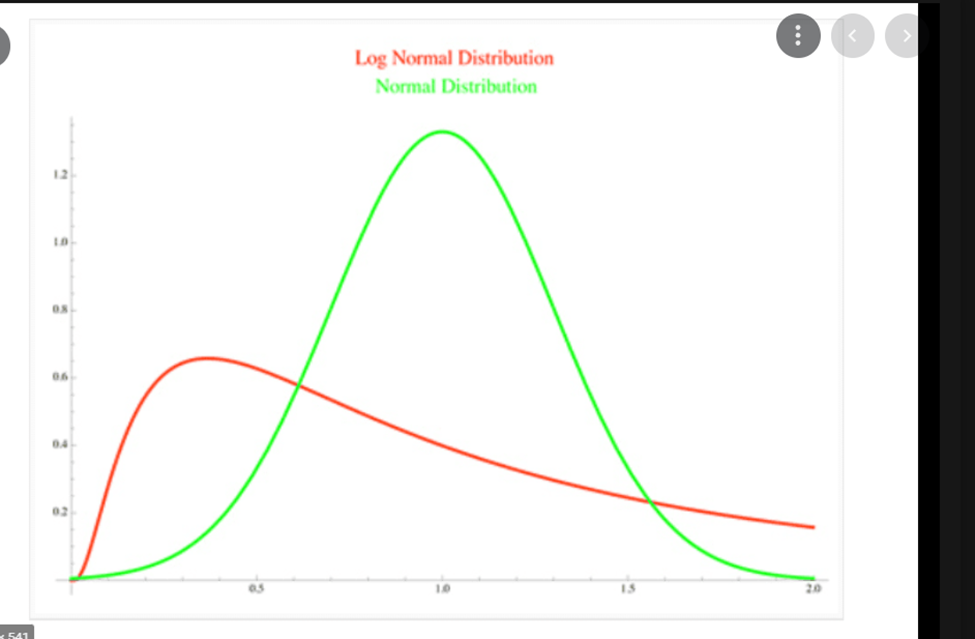
- The lognormal distribution differs from the normal distribution in several ways. A major difference is in its shape: the normal distribution is symmetrical, whereas the lognormal distribution is not. Because the values in a lognormal distribution are positive, they create a right-skewed curve.
- The
lognormal distribution model is considered to be very useful in the fields
of medicine, economics, and engineering.
- Overall the
log-normal distribution plots the log of random variables from a normal
distribution curve.
Right skewed
distributions with low mean values, large variance, and all positive values
often fit this distribution. Example of lognormal distribution in nature are
the amount of rainfall, milk production by cows, and for most natural growth
processes, where the growth rate is independent of size.
·
This skewness is important in
determining which distribution is appropriate to use in investment
decision-making. A further distinction is that the values used to derive a
lognormal distribution are normally distributed.
·
Let's clarify with an example. An investor
wants to know an expected future stock price. Since stocks grow at a
compounded rate, they need to use a growth factor. To calculate possible
expected prices, they will take the current stock price and multiply it by
various rates of return (which are mathematically derived exponential factors based on compounding), which are assumed to be normally
distributed. When the investor continuously compounds the returns, they
create a lognormal distribution. This distribution is always positive even if
some of the rates of return are negative, which will happen 50% of the time in
a normal distribution. The future stock price will always be positive because
stock prices cannot fall below $0.
No comments:
Post a Comment